What Is a Steam Lock?
What is Steam Lock?
In the operation of steam equipment, unexplained temperature drops often indicate the presence of water accumulation within the system. This phenomenon, known as "steam lock," occurs when steam and condensate mix and enter the steam trap, preventing the steam from being discharged. As a result, the steam becomes trapped inside the steam trap and the preceding pipeline segment, leading to condensate accumulating within the equipment. Consequently, steam cannot enter the equipment to provide the necessary heating, causing a temperature drop.
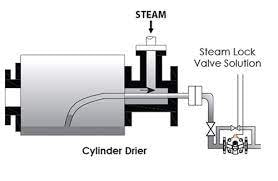
Conditions Leading to Steam Lock
Steam lock is not caused by the steam trap itself but rather by the structural characteristics of the equipment or an improper layout of the pipelines before and after the steam trap. The following scenarios can lead to the formation of a steam lock:
Sulfurization Machines, Drum Dryers, Elongated Tube Heat Exchangers, and Other Equipment with Siphon Drainage Systems: These types of equipment are particularly prone to steam lock due to their design, which can cause condensate to accumulate and mix with the steam.
Steam Traps Installed at the Top of Vertical Pipes: When a steam trap is positioned at the highest point of a vertical pipe, steam lock can occur because condensate can accumulate in the vertical section, obstructing the steam flow.
Undersized Piping Before the Steam Trap: If the pipeline leading to the steam trap is too small, it can restrict the flow of condensate, causing it to mix with the steam and create a steam lock.
Steam Traps Installed Far from the Steam-Using Equipment: When there is a significant distance between the steam trap and the equipment using the steam, steam lock can occur due to the increased likelihood of condensate accumulation in the pipeline.
Detailed Analysis and Practical Implications
Equipment-Specific Issues
For equipment such as sulfurization machines, drum dryers, and elongated tube heat exchangers, the design often involves complex pathways and siphon drainage systems. These features, while essential for their operation, can inadvertently lead to pockets where condensate gathers. Over time, this condensate can mix with incoming steam, leading to steam lock situations that hinder the efficient operation of the equipment.
Installation-Related Issues
Vertical Installation Problems: Steam traps installed at the top of vertical pipes face a unique challenge. Gravity causes condensate to naturally accumulate at the lowest points. When the steam trap is positioned vertically high, it can lead to a situation where condensate cannot be efficiently removed, causing a mix with steam and resulting in steam lock.
Explore more:How to set up a chakki atta plant?
Pipeline Sizing: The diameter of pipelines leading to the steam trap is crucial. Undersized pipes cannot handle the volume of condensate, which can cause a backup and mixing with steam. Proper sizing ensures that condensate is swiftly and efficiently moved out of the system, preventing steam lock.
Distance from Equipment: The farther the steam trap is from the equipment using the steam, the greater the chance for condensate to accumulate and create a steam lock. This issue can be mitigated by strategically placing steam traps closer to the equipment or by redesigning the pipeline layout to facilitate better drainage.
Preventing Steam Lock
Preventing steam lock involves addressing both equipment design and installation practices. Here are some strategies:
Review and Modify Equipment Design: For equipment prone to steam lock, consider design modifications that facilitate better drainage and reduce condensate accumulation. This might include altering the pathway of the steam and condensate or integrating additional drainage points.
Optimizing Pipeline Layout: Ensure that pipelines are appropriately sized and routed to facilitate efficient condensate removal. Avoid positioning steam traps at high points in vertical pipes unless necessary adjustments are made to manage condensate flow effectively.
Strategic Placement of Steam Traps: Place steam traps as close to the steam-using equipment as possible to minimize the distance condensate travels. This reduces the likelihood of condensate mixing with steam and causing a steam lock.
Regular Maintenance and Monitoring: Implement a routine maintenance schedule to check for signs of condensate accumulation and ensure steam traps are functioning correctly. Use monitoring systems to detect temperature drops or pressure changes that might indicate steam lock.
Conclusion
Understanding steam lock and its causes is essential for maintaining efficient steam system operations. By addressing equipment design issues, optimizing pipeline layouts, and ensuring proper steam trap placement, steam lock can be effectively prevented. This not only enhances the efficiency of steam equipment but also ensures consistent operational performance, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. Through careful planning and regular maintenance, steam lock can be managed, ensuring that steam systems operate at their best.


