Ethylene Glycol Diacetate: Properties, Applications, and Safety Considerations
Ethylene Glycol Diacetate (EGDA) is an organic compound that belongs to the family of glycol ethers. It is derived from the reaction of ethylene oxide with acetic acid, resulting in a versatile chemical compound with numerous industrial applications. In this article, we explore the properties, applications, and safety considerations associated with Ethylene Glycol Diacetate.
Properties of Ethylene Glycol Diacetate:
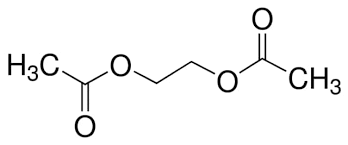
Chemical Structure: Ethylene Glycol Diacetate is a clear, colorless liquid with a molecular formula of C6H10O4. It consists of two acetyl groups attached to an ethylene glycol backbone.
Solubility: EGDA is miscible with many organic solvents, including alcohols, ketones, esters, and glycol ethers. It exhibits limited solubility in water but can form stable emulsions.
Boiling Point: The boiling point of EGDA is approximately 192°C (378°F), making it suitable for applications requiring high-temperature stability.
Applications of Ethylene Glycol Diacetate:
Industrial Solvents: EGDA serves as a solvent in various industrial applications. It is commonly used in the manufacturing of coatings, paints, and inks, where it acts as a carrier and viscosity modifier. EGDA also finds application as a solvent in adhesives, cleaning agents, and specialty chemical formulations.
Chemical Intermediates: Ethylene Glycol Diacetate serves as a versatile chemical intermediate in the synthesis of other compounds. It can undergo various reactions, such as esterification and transesterification, to produce derivatives used in the production of pharmaceuticals, flavors, fragrances, and plasticizers.
Coalescing Agent: EGDA acts as a coalescing agent in water-based coatings. It promotes film formation and fusion of polymer particles, resulting in improved coating quality, adhesion, and durability.
Agricultural Applications: Ethylene Glycol Diacetate is utilized in the agricultural industry as a solvent for pesticides and herbicides. It aids in the dispersion and delivery of active ingredients, enhancing the effectiveness of agricultural formulations.
Safety Considerations:
Health Hazards: Ethylene Glycol Diacetate is classified as a hazardous substance. It may cause irritation to the skin, eyes, and respiratory system upon direct contact or inhalation of vapors. Prolonged or repeated exposure may lead to more severe health effects. Adequate ventilation, protective clothing, and personal protective equipment should be used when handling EGDA.
Flammability: Ethylene Glycol Diacetate is a combustible liquid and should be stored away from open flames or sources of ignition. Suitable fire precautions should be taken when handling and storing EGDA to prevent fire hazards.
Environmental Impact: EGDA may have adverse effects on aquatic life if released into water bodies. Proper containment, handling, and disposal practices should be followed to minimize environmental impact.
Regulatory Compliance: It is essential to adhere to local regulations and safety guidelines when using Ethylene Glycol Diacetate. Employers should provide appropriate training and ensure compliance with occupational health and safety standards.Learn more


